health and fitness articles, health and fitness blog topics, health and fitness articles, health care tips, male and female sex hormones, male and female reproductive system
Sunday, July 30, 2023
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction: Causes, Treatments, and Coping Strategies
Introduction:
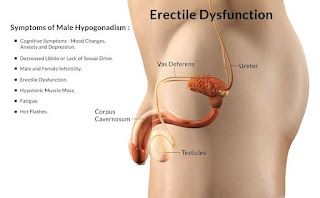
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a prevalent condition affecting millions of men worldwide. Also known as impotence, it is characterized by the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual intercourse. While it can be a sensitive topic, understanding the causes, treatments, and coping strategies for ED is essential for affected individuals and their partners. This article aims to shed light on this common condition and provide valuable insights into managing its effects on physical and emotional well-being.
1. Causes of Erectile Dysfunction:
ED can be caused by various physical, psychological, and lifestyle factors. Physical causes may include cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, hormonal imbalances, obesity, and neurological disorders. Psychological factors like stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship problems can also contribute to ED. Additionally, habits like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use can exacerbate the condition.
2. Medical Treatments and Therapies:
The first step in treating ED is identifying the underlying cause. Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for an accurate diagnosis. Depending on the cause, treatment options may include oral medications, such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), or vardenafil (Levitra), which enhance blood flow to the penis. Other treatments like vacuum erection devices, penile implants, and injections can also be considered, depending on individual cases.
3. Lifestyle Changes for ED Management:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly improve ED symptoms. Regular exercise can enhance cardiovascular health and blood flow, contributing to better erectile function. Maintaining a balanced diet, managing weight, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also positively impact ED. Additionally, open communication with one's partner about the issue can alleviate stress and foster a supportive environment.
4. Psychological Support and Counseling:
Since psychological factors can play a significant role in ED, seeking professional counseling or therapy might be beneficial. Addressing underlying emotional issues can lead to improvements in sexual function. Couples therapy can also help partners navigate the challenges that ED may present in their relationship.
5. Promising Research and Future Outlook:
Ongoing research in the field of ED continues to yield promising results. Advancements in medical science have led to novel therapies and treatment options for ED. Understanding the complexities of the condition is crucial to developing more effective interventions in the future.
Conclusion:
Erectile dysfunction is a common condition that affects many men and can have a significant impact on their quality of life and overall well-being. However, it is essential to recognize that ED is a medical condition and not a reflection of one's masculinity or worth. Seeking professional help and adopting a proactive approach to managing the condition can lead to positive outcomes. By understanding the causes, treatments, and coping strategies for ED, individuals and their partners can work together to navigate this challenging but manageable condition. Remember, seeking support and maintaining open communication are vital aspects of overcoming erectile dysfunction and enjoying a fulfilling and satisfying sex life.
Saturday, July 29, 2023
Breast Cancer: Understanding, Preventing, and Fighting the Silent Killer
Introduction
Breast cancer is a devastating disease that affects millions of women worldwide, causing physical and emotional distress for both patients and their loved ones. Despite significant advancements in medical science, breast cancer remains a significant public health challenge. This article aims to shed light on breast cancer, exploring its causes, risk factors, early detection, treatment options, and the importance of awareness and prevention.
Understanding Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the cells of the breast tissue. It usually begins in the milk ducts (ductal carcinoma) or the lobules (lobular carcinoma) and can spread to other parts of the body if left untreated. Although it predominantly affects women, men can also develop breast cancer, though it is less common.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of breast cancer is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a result of a combination of genetic, hormonal, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Some common risk factors include:
1. Age: The risk of breast cancer increases with age, especially after the age of 50.
2. Family history and genetics: Women with close relatives (mother, sister, daughter) who have had breast cancer are at higher risk. Inherited gene mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, are also associated with an increased risk.
3. Hormone-related factors: Early menstruation, late menopause, and hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can influence the risk of breast cancer.
4. Personal history of breast cancer: A woman who has previously had breast cancer has a higher risk of developing it again in the same or opposite breast.
5. Lifestyle factors: Obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, lack of physical activity, and a high-fat diet may increase the risk of breast cancer.
Early Detection and Diagnosis
Early detection is crucial in improving breast cancer outcomes. Regular breast self-examinations, clinical breast exams, and mammograms are essential for detecting any abnormalities in the breast tissue. Mammography is a widely used screening tool that can detect tumors before they can be felt manually.
It’s essential for women to be proactive about their breast health and promptly report any changes or concerns to their healthcare providers. Early diagnosis increases the chances of successful treatment and may offer less aggressive treatment options.
Treatment Options
The treatment plan for breast cancer varies depending on the stage, type, and individual health factors of the patient. The primary treatment options include:
1. Surgery: Surgery involves the removal of the tumor and, in some cases, the entire breast (mastectomy). Breast-conserving surgery, or lumpectomy, aims to remove only the tumor while preserving the breast.
2. Radiation therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells after surgery, reducing the risk of cancer recurrence.
3. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. It is often recommended when cancer has spread beyond the breast.
4. Hormone therapy: For hormone receptor-positive breast cancers, hormone therapy is used to block the effects of estrogen or progesterone on cancer cells.
5. Targeted therapy: Targeted drugs aim to block specific abnormalities in cancer cells, limiting damage to healthy cells.
The Importance of Awareness and Prevention
Breast cancer awareness plays a crucial role in promoting early detection and prompt treatment. Regular screening and open conversations about breast health are essential in empowering women to take charge of their well-being.
Preventive measures can also significantly reduce the risk of breast cancer. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding smoking can all contribute to lowering the risk.
Conclusion.
Breast cancer is a formidable opponent that affects millions of women worldwide. Early detection and timely treatment can make a significant difference in the outcomes for breast cancer patients. By spreading awareness, supporting ongoing research, and encouraging healthy lifestyle choices, we can collectively work towards a future where breast cancer is a preventable and manageable condition. Remember, knowledge is power, and taking control of our breast health is one of the most proactive steps we can take in the fight against breast cancer.
Thursday, July 27, 2023
Brian Tumor
A brain tumor refers to an abnormal growth of cells within the brain or its surrounding structures. Tumors can be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). The development of a brain tumor can have various causes, and its impact on an individual's health and well-being depends on its size, location, and type.
Types of Brain Tumors:
1. Primary Brain Tumors: These originate in the brain tissue itself and can be classified based on the type of cells they arise from. Some common types include gliomas, meningiomas, pituitary adenomas, and schwannomas.
2. Secondary (Metastatic) Brain Tumors: These are tumors that have spread to the brain from cancerous cells originating in other parts of the body. They are more common than primary brain tumors.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact causes of brain tumors are often unknown, but certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of their development. These risk factors may include exposure to ionizing radiation, a family history of brain tumors, certain genetic conditions, and a compromised immune system.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of a brain tumor can vary widely depending on its size and location. Some common signs and symptoms include:
1. Headaches: Persistent and severe headaches, often worse in the morning or upon waking up.
2. Seizures: Uncontrolled electrical disturbances in the brain that may lead to convulsions or loss of consciousness.
3. Cognitive and Behavioral Changes: Memory problems, confusion, mood swings, and personality changes.
4. Motor and Sensory Deficits: Weakness, numbness, or tingling in the limbs, difficulty balancing, and coordination issues.
5. Vision or Hearing Problems: Blurred or double vision, hearing loss, or other sensory disturbances.
6. Nausea and Vomiting: Especially in the morning or with changes in head position.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing a brain tumor involves a series of tests and examinations, including neurological exams, imaging studies like MRI or CT scans, and in some cases, a biopsy to determine the tumor's type and grade.
Treatment:
The treatment for a brain tumor depends on its type, size, location, and the patient's overall health. Treatment options may include:
1. Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor is often the first-line treatment if feasible and safe.
2. Radiation Therapy: The use of high-energy rays to kill or shrink cancer cells.
3. Chemotherapy: The administration of drugs to kill or slow down tumor growth.
4. Targeted Therapies: Drugs designed to specifically target certain mutations or characteristics of the tumor cells.
5. Supportive Care: Managing symptoms and providing supportive measures to improve the patient's quality of life.
Prognosis:
The prognosis for brain tumor patients varies widely and depends on factors such as tumor type, stage, location, age of the patient, and overall health. Some tumors can be successfully treated or managed, leading to good outcomes, while others may be more challenging to control.
Coping and Support:
A brain tumor diagnosis can be emotionally and physically challenging for both patients and their loved ones. Support from healthcare professionals, counselors, support groups, and family members is essential to help patients cope with the diagnosis, treatment, and potential long-term effects.
It's crucial to remember that every brain tumor case is unique, and individual outcomes may differ significantly. Early detection, timely intervention, and ongoing research into brain tumor treatments are vital to improving outcomes and the quality of life for those affected.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
A complete and detailed discussion on the Harms of Obesity.
Here are the disadvantages of obesity : Physical Health Risks 1. *Diabetes*: Obesity is a major risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes...

-
Definition of ascites is the accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal or abdominal cavity now the fluid which accumulates can either be t...
-
A brain tumor refers to an abnormal growth of cells within the brain or its surrounding structures. Tumors can be either benign (non-cance...
-
Introduction Breast cancer is a devastating disease that affects millions of women worldwide, causing physical and emotional distress for ...